-
Cryptocurrencies
-
Exchanges
-
Media
All languages
Ontology (ONT) is a new generation of public basic chain projects and a distributed trust collaboration platform, including a complete distributed ledger and smart contract system support.
The Ontology architecture supports the public chain network system. In addition to providing basic public chain services, it also supports the customization of public chains for different applications through the Ontology blockchain framework, and chain-network collaboration through different protocol groups.
On the base layer, Ontology will continue to provide common modules in various distributed applications, such as distributed identity framework, distributed data exchange protocol, etc. to support distributed trust collaboration components, and will continue to expand according to application requirements New common modules.
• Scalable lightweight general-purpose smart contracts.
• Extensible WASM contract support.
♦Cross-chain interaction protocol.
• Multiple encryption algorithms are supported.
•Highly optimized transaction processing speed.
• P2P connection link encryption.
•Support multiple consensus algorithms.
• Fast block generation time.
1. Ontology Smart Contract
Ontology smart contract is a complete system integrating multi-function, lightweight, high availability, concurrent, multi-language, cross-contract, and cross-virtual machine. Ontology smart contracts support a variety of mainstream development languages, such as C#, Python, etc. Developers can easily develop Ontology smart contracts without learning new languages. In the future, more mainstream development languages will be supported, including: Java , C++ , Rust , Go , JavaScript , etc.
Ontology smart contracts have the characteristics of determinism, high performance, and scalability, and include two modules: interactive services and virtual machines.
The interaction service provides the interaction between the virtual machine and the blockchain ledger.
The virtual machine provides an operating environment for smart contracts. Interactive services include native services and NEO virtual machine services.
Native services provide the implementation of special smart contracts on the underlying chain, which can be used quickly and easily.
The NEO virtual machine service provides an API for external access to the NEO virtual machine, which can enhance the calling function of smart contracts.
2. Ontology's trust ecosystem
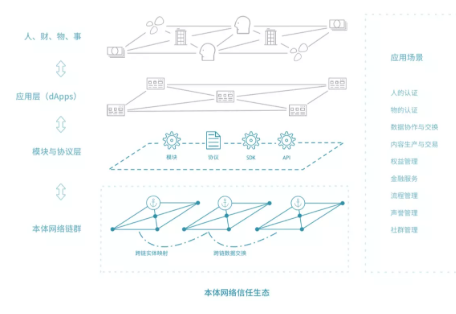
Figure 1 Ontology's trust ecosystem
As shown in the trust ecological diagram of the Ontology network above, people, money, and things almost cover the source of financial transactions, from the transaction behavior outside the chain to the application layer of the Ontology network for interconnection, and modules and protocols are guaranteed transactions. To be sure, put the sdk and api together to form a channel that extends in all directions, and can use the modules and protocols on the chain to capture information resources and other applications outside the chain, so as to ensure the inclusiveness of the Ontology network and the powerful and diverse functions change. Its biggest core lies in two points: building a trust bridge inside and outside the chain, forming rights confirmation, protocols and modules, sdk and api as open source tools are all for it.
3. Ontology's trust network
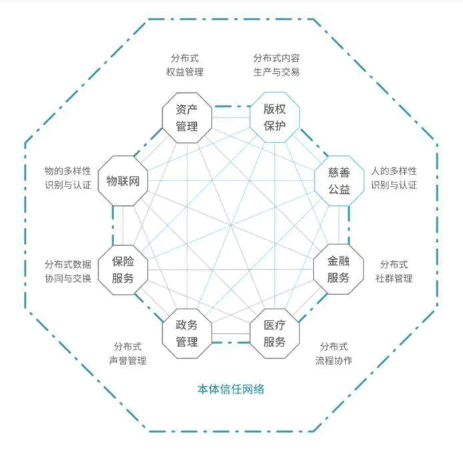
Figure 2 Ontology trust network
On the basis of trust, a variety of tools are used to realize the interconnection between the chain and the outside of the chain. This process is completed within the framework of the system, and all the user needs to do is to complete some simple basic operations. The use of ontology network. Just like driving a car, you don't need to clearly understand how the car is assembled and designed. You only need to take a driver's license to make the car a tool or carrier to achieve your goals. Ontology is the manufacturer that designs and assembles the vehicle. Of course, in addition to trust in legal attributes, there is also a part of trust from its consensus mechanism.
4. Ontology's consensus mechanism VBFT
VBFT is a new consensus algorithm that combines PoS, VRF (Verifiable Random Function) and BFT (Byzantine Fault Tolerance). In the VBFT consensus algorithm, Ontology ONT nodes first need to pay a deposit to apply to become a consensus node, and randomly select three types of nodes from all consensus nodes through verifiable random numbers: candidate nodes, verification nodes and confirmation nodes. The candidate node proposes a candidate block, the verification node verifies the candidate block, and the confirmation node completes the block consensus after endorsement voting on the verification result.
The VBFT consensus does not need to be confirmed by all nodes in the entire network to form a consensus. Instead, in the form of mortgage, use the random selectivity of VRF (Verifiable Random Function) to select a part of nodes in three groups among many nodes for verification, so as to achieve expansion and increase the speed. At the same time, this combination of randomness and PoS consensus ensures the anti-attack (security) of the algorithm, and the two-thirds fault-tolerant verification method of BFT can quickly reach a block consensus. It has the trust, security, speed, stickiness and other elements of the consensus.
V. Ontology Network Technology Architecture
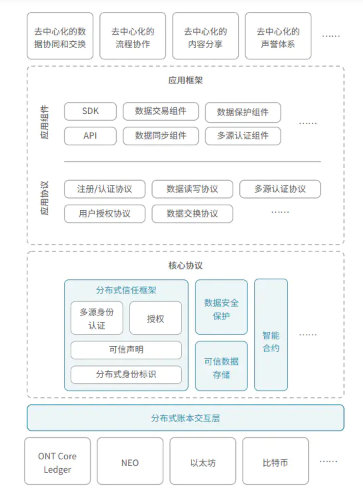
Figure 3 Ontology Network Technology Architecture
The bottom layer of the Ontology network provides a complete distributed ledger system, including a complete smart contract system and security system. At the same time, the Ontology network abstracts the underlying complex technical system and architecture system, realizes distributed entity management and multi-dimensional authentication protocols that are compatible with various major protocols and cryptographic standards, and supports all kinds of heterogeneous blockchains and traditional blockchains. Cross-chain and cross-system interactive mapping of information systems.
Ontology also provides technical systems such as secure data storage, heterogeneous smart contracts, hardware key management, and encrypted data analysis. As an application platform, the entire network can support the construction of various application services, especially decentralized applications. On this basis, Ontology Network provides a series of application frameworks, including distributed data exchange protocols, distributed process management protocols, etc., and further supports the realization of various upper-layer applications through general APIs, SDKs, and various application function components.
Related literature:
https://ont.io/
https://ont.io/wp/Ontology-Introductory-White-Paper-ZH. pdf











